Access to healthcare in rural America remains a significant challenge for millions living in remote and underserved areas. While rural regions are known for their expansive landscapes and close-knit communities, they face persistent issues in securing quality healthcare. Rural residents often encounter barriers such as a lack of healthcare providers, limited specialized services, and lengthy travel times to the nearest medical facility. These obstacles contribute to notable disparities in health outcomes, with rural populations experiencing higher rates of chronic illnesses, reduced life expectancy, and increased susceptibility to preventable conditions.
Socioeconomic factors also play a critical role, as lower income levels, higher rates of uninsured individuals, and limited transportation options further complicate access to care. The recent closures of rural hospitals have intensified these problems, leaving many areas without essential medical services and emergency care. Addressing these challenges demands a comprehensive strategy, including expanding telehealth options, boosting funding for rural healthcare infrastructure, and encouraging healthcare professionals to serve in underserved regions.
Improving healthcare access in rural America is vital for enhancing individual well-being and sustaining the vitality of these communities. By investing in targeted solutions to meet the unique needs of rural populations, we can strive for a more equitable and effective healthcare system.
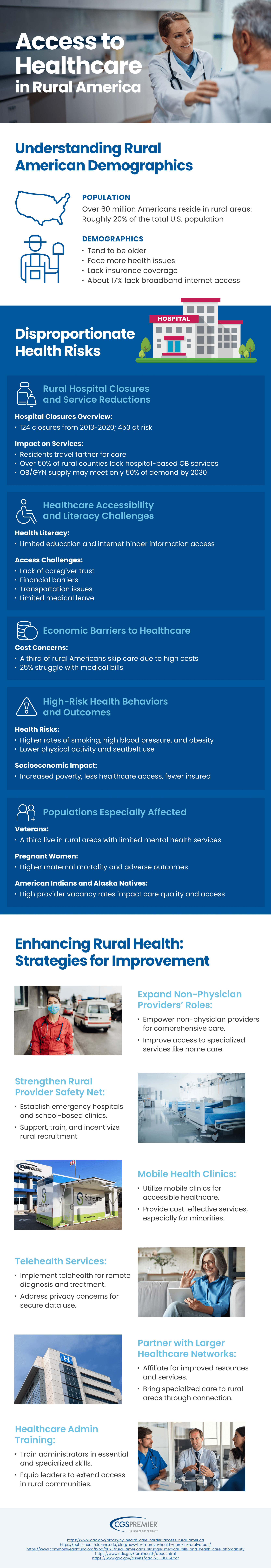
Infographic provided by CGS Premier, a provider of mobile healthcare vans
Table of Contents
Understanding the Healthcare Challenges in Rural America
Rural healthcare systems are vastly different from their urban counterparts. The populations in these areas are generally older, less affluent, and more prone to chronic diseases. With fewer hospitals and clinics per capita, those living in rural communities often have to travel long distances for care, and in many cases, they are uninsured or underinsured, further limiting their access. These challenges combine to create a healthcare system that struggles to meet the needs of its residents.
Geographic Barriers to Healthcare Access
One of the most significant obstacles facing rural Americans is their physical distance from healthcare facilities. While urban residents may have several hospitals or clinics within a few miles, rural residents often live hours away from the nearest hospital. This can make seeking regular medical attention, or even emergency care, difficult and sometimes dangerous.
Adding to this issue is the lack of reliable public transportation in many rural areas. Without easy access to transportation, elderly or low-income individuals face even greater barriers to receiving timely medical attention, especially for follow-up visits or specialist appointments.
Economic Factors Limiting Healthcare Access
Rural communities often face economic difficulties, and this reality plays a large role in limiting access to healthcare. Rural residents tend to have lower incomes and higher rates of poverty compared to urban populations, which impacts their ability to afford healthcare services, including insurance.
Lack of Health Insurance Coverage
Many rural Americans are either underinsured or uninsured, which is a significant barrier to healthcare access. Although Medicaid and Medicare cover many low-income or elderly individuals, not all rural residents qualify for these programs, and others fall into coverage gaps. Without sufficient insurance, people are less likely to seek preventative care, leading to worse health outcomes in the long run.
High Out-of-Pocket Costs
Even for those with insurance, high out-of-pocket costs for medical treatments and prescription drugs can be prohibitive. Many rural residents face difficult decisions, such as whether to pay for necessary medications or other essentials like groceries and housing. This financial burden leads to delayed treatments, which can worsen medical conditions over time.
Shortage of Healthcare Providers in Rural Areas
One of the most pressing issues in rural healthcare is the lack of healthcare providers. Rural areas face a critical shortage of both primary care physicians and specialists, which can lead to long wait times and limited access to specialized care.
Primary Care Physician Shortages
Many rural counties in the U.S. lack even a single primary care physician. Those who are available are often overworked, leading to long wait times and burnout among healthcare providers. The shortage of primary care physicians is particularly troubling because these doctors serve as the first point of contact for most patients, providing essential preventive care and managing chronic conditions.
Shortage of Specialists
In addition to a lack of general practitioners, rural areas also suffer from a severe shortage of specialists, including cardiologists, oncologists, and pediatricians. Patients in need of specialized care often have to travel significant distances or go without treatment entirely. This shortage of specialists makes it difficult to manage complex health conditions, contributing to poorer health outcomes in rural populations.
The Role of Telemedicine in Addressing Rural Healthcare Gaps
Telemedicine has emerged as a promising solution for addressing some of the healthcare challenges in rural America. By leveraging technology, telehealth services allow rural patients to connect with healthcare providers, including specialists, without the need for long-distance travel.
Expanding Access to Specialists Through Telehealth
For rural patients who need specialized care, telemedicine offers an invaluable resource. Telehealth consultations allow patients to receive expert advice and treatment from specialists located hundreds of miles away. This reduces the burden of travel and ensures that rural populations have access to the same level of care as urban residents. Many healthcare systems are implementing telehealth programs that have proven successful in expanding access to high-quality medical care in rural regions.
Telemedicine for Mental Health Services
Mental health is another area where telemedicine is making a significant impact. In rural areas, where mental health services are often scarce, teletherapy is providing an accessible way for patients to receive counseling and support. Given the higher rates of depression, anxiety, and suicide in rural populations, the rise of teletherapy could play a critical role in improving mental health outcomes.
Government Programs and Policies Aimed at Improving Rural Healthcare
Several government initiatives have been put in place to address healthcare disparities in rural America. These programs aim to increase the number of healthcare providers in rural areas, provide funding for rural health clinics, and improve overall healthcare access.
The National Health Service Corps
The National Health Service Corps is a federal program that incentivizes healthcare professionals to work in rural and underserved areas by offering loan forgiveness and scholarships. While this program has helped bring medical professionals to some rural areas, the need for doctors and nurses still far exceeds supply.
Rural Health Clinics (RHCs) and Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs)
RHCs and FQHCs play an essential role in providing care to rural populations. These facilities receive federal funding to serve low-income, uninsured, and underinsured individuals. However, funding challenges and sustainability issues often limit their ability to fully meet the healthcare needs of rural communities.
Community-Based Solutions to Healthcare Access
In addition to government programs, local community initiatives are also helping to bridge the healthcare gap. Nonprofits and community health organizations play a key role in providing services such as free clinics, mobile health units, and health education programs.
Addressing Social Determinants of Health in Rural Communities
Healthcare access in rural areas is not solely a medical issue. Social determinants such as education, housing, and nutrition also play a significant role in determining health outcomes.
Improving Health Literacy
Health literacy is often lower in rural areas, meaning that many people lack the knowledge needed to make informed healthcare decisions. Improving health education can empower individuals to take better care of themselves and access the services they need.
Addressing Food Deserts and Nutrition Issues
Many rural areas are also considered “food deserts,” where residents have limited access to fresh, healthy food. Poor nutrition is a major factor in the prevalence of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease in rural populations. Addressing these food access issues is essential for improving the overall health of rural communities.
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Rural Healthcare
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed and deepened many of the existing healthcare disparities in rural areas. With fewer healthcare facilities and resources, rural communities were hit hard by the virus, and the long-term effects are still being felt. However, the pandemic also accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, which has the potential to address some of these disparities moving forward.
The Future of Healthcare in Rural America
Looking ahead, emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), telemedicine, and mobile health clinics will continue to play a crucial role in bridging the healthcare gap. However, long-term solutions will also require sustained investment in rural infrastructure, education, and workforce development to ensure that everyone, regardless of where they live, has access to quality healthcare.
Conclusion
Access to healthcare in rural America remains a pressing issue, but with targeted interventions and the right resources, these gaps can be addressed. From improving the recruitment of healthcare professionals to leveraging technology and expanding community-based solutions, there are many ways to improve rural healthcare. It will take a concerted effort from government agencies, healthcare organizations, and communities to ensure that rural populations receive the care they need and deserve.
FAQs
Why is there a shortage of healthcare providers in rural areas?
Rural areas often struggle to attract healthcare providers due to factors like isolation, lower pay, and fewer professional opportunities. This shortage is exacerbated by the high demand for services.
What role does telemedicine play in rural healthcare?
Telemedicine helps bridge the gap in access by allowing rural patients to consult with healthcare providers, including specialists, without needing to travel long distances.
How does transportation affect healthcare access in rural communities?
Lack of reliable transportation in rural areas makes it difficult for residents, especially the elderly and low-income individuals, to access healthcare facilities, leading to delayed or missed treatments.
Are there government programs helping rural healthcare access?
Yes, programs like the National Health Service Corps and funding for Rural Health Clinics aim to improve healthcare access in rural areas, though challenges remain in reaching all communities.
What are some community-driven solutions to healthcare gaps in rural areas?
Local initiatives like free clinics, mobile health units, and partnerships with nonprofits help provide essential healthcare services and education to underserved rural populations.
